Product Description
|
Model |
BST400AFZ/BSZ |
|
Voltage/frequency (V/Hz) |
220-240V/50Hz 100v-120v/60Hz |
|
Input power(W) |
≤300 |
|
Speed (r/min) |
≥1350 1650 |
|
Primary vacuumKPa |
-94KPa |
|
Secondary vacuumKPa |
-100KPa |
|
Restart pressure (KPa) |
0KPa |
|
Rated volume flow (m3/h) |
≥7.0m3/h @0KPa; |
|
Noise dB(A) |
≤55dB(A) |
|
Ambient temperature ºC |
-5~40 ºC |
|
Insulation Class |
B |
|
Cold insulation resistance (MΩ) |
≥100MΩ |
|
Voltage resistance |
1500V/50Hz 1min (No breakdown) |
|
Thermal protector |
Automatic reset 135±5ºC |
|
Capacitance (μF) |
15μF±5% 45μF±5% |
|
Net weight (Kg) |
7.8Kg |
|
Installation Dimensions (mm) |
203.2×88.9mm(Install thread 4-M6) |
|
External Dimensions (mm) |
244.5*128*177mm |
| Typical application | |
| Respirator (ventilator) | oxygenerator |
| Disinfectant sprayer | Blood analyzer |
| Clinical aspirator | Dialysis / hemodialysis |
| Dental vacuum drying oven | Air suspension system |
| Vending machines / coffee blenders and coffee machines | Massage chair |
| Chromatographic analyzer | Teaching instrument platform |
| On board access control system | Airborne oxygen generator |
Why choose CZPT air compressor
1. It saves 10-30% energy than the air compressor produced by ordinary manufacturers.
2. It is widely used in medical oxygen generator and ventilator .
3. A large number of high-speed train and automobile application cases, supporting – 41 to 70 ºC, 0-6000 CZPT above sea level .
4. Medium and high-end quality, with more than 7000 hours of trouble free operation for conventional products and more than 15000 hours of trouble free operation for high-end products.
5. Simple operation, convenient maintenance and remote guidance.
6. Faster delivery time, generally completed within 25 days within 1000 PCs.
Machine Parts
Name: Motor
Brand: COMBESTAIR
Original: China
1.The coil adopts the fine pure copper enameled wire, and the rotor adopts the famous brand silicon steel sheet such as ZheJiang baosteel.
2.The customer can choose the insulation grade B or F motor according to What he wants.
3.The motor has a built-in thermal protector, which can select external heat sensor.
4.Voltage from AC100V ~120V, 200V ~240V, 50Hz / 60Hz, DC6V~200V optional ; AC motor can choose double voltage double frequency ; DC Motor can choose the control of the infinitely variable speed.
Machine Parts
Name: Bearing
Brand: ERB , CZPT , NSK
Original: China ect.
1.Standard products choose the special bearing ‘ERB’ in oil-free compressor, and the environment temperature tolerance from -50ºC to 180 ºC . Ensure no fault operation for 20,000 hours.
2.Customers can select TPI, NSK and other imported bearings according to the working condition.
Machine Parts
Name: Valve plates
Brand: SANDVIK
Original: Sweden
1.Custom the valve steel of Sweden SANDVIK; Good flexibility and long durability.
2.Thickness from 0.08mm to 1.2mm, suitable for maximum pressure from 0.8 MPa to 1.2 MPa.
Machine Parts
Name: Piston ring
Brand: COMBESTAIR-OEM , Saint-Gobain
Original: China , France
1.Using domestic famous brand–Polytetrafluoroethylene composite material; Wear-resistant high temperature; Ensure more than 10,000 hours of service life.
2.High-end products: you can choose the ST.gobain’s piston ring from the American import.
| serial number |
Code number | Name and specification | Quantity | Material | Note |
| 1 | 212571109 | Fan cover | 2 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 2 | 212571106 | Left fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 3 | 212571101 | Left box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 4 | 212571301 | Connecting rod | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 5 | 212571304 | Piston cup | 2 | PHB filled PTFE | |
| 6 | 212571302 | Clamp | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 7 | 7050616 | Screw of cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M6•16 |
| 8 | 212571501 | Air cylinder | 2 | Thin wall pipe of aluninun alloy 6A02T4 | |
| 9 | 17103 | Seal ring of Cylinder | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 10 | 212571417 | Sealing ring of cylinder cover | 2 | Silicone rubber | |
| 11 | 212571401 | Cylinder head | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 12 | 7571525 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 12 | M5•25 | |
| 13 | 17113 | Sealing ring of connecting pipe | 4 | Silicong rubber | |
| 14 | 212571801 | Connecting pipe | 2 | Aluminum and aluminum alloy connecting rod LY12 | |
| 15 | 7100406 | Screw of Cross head | 4 | 1Cr13N19 | M4•6 |
| 16 | 212571409 | Limit block | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 17 | 000402.2 | Air outlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 18 | 212571403 | valve | 2 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL102 | |
| 19 | 212571404 | Air inlet valve | 2 | 7Cr27 quenching steel belt of The Swedish sandvik | |
| 20 | 212571406 | Metal gasket | 2 | Stainless steel plate of heat and acidresistance | |
| 21 | 212571107 | Right fan | 1 | Reinforced nylon 1571 | |
| 22 | 212571201 | Crank | 2 | Gray castiron H20-40 | |
| 23 | 14040 | Bearing 6006-2Z | 2 | ||
| 24 | 70305 | Tighten screw of inner hexagon flat end | 2 | M8•8 | |
| 25 | 7571520 | Screw of inner hexagon Cylinder head | 2 | M5•20 | |
| 26 | 212571102 | Right box | 1 | Die-cast aluminum alloy YL104 | |
| 27 | 6P-4 | Lead protective ring | 1 | ||
| 28 | 7095712-211 | Hexagon head bolt | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•152 |
| 29 | 715710-211 | Screw of Cross head | 2 | Carbon structural steel of cold heading | M5•120 |
| 30 | 16602 | Light spring washer | 4 | ø5 | |
| 31 | 212571600 | Stator | 1 | ||
| 32 | 70305 | Lock nut of hexagon flange faces | 2 | ||
| 33 | 212571700 | Rotor | 1 | ||
| 34 | 14032 | Bearing 6203-2Z | 2 |
FAQ
Q1: Are you factory or trade company?
A1: We are factory.
Q2: What the exactly address of your factory?
A2: Our factory is located in Linbei industrial area No.30 HangZhou City of ZHangZhoug Province, China
Q3: Warranty terms of your machine?
A3: Two years warranty for the machine and technical support according to your needs.
Q4: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
A4: Yes, of course.
Q5: How long will you take to arrange production?
A5: Generally, 1000 pcs can be delivered within 25 days
Q6: Can you accept OEM orders?
A6: Yes, with professional design team, OEM orders are highly welcome
Q7:Can you accept non-standard customization?
A7:We have the ability to develop new products and can customize, develop and research according to your requirements
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Remote Guided Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Principle: | Mixed-Flow Compressor |
| Samples: |
US$ 60/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
Disadvantages of using a vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that pulls gas molecules out of a volume and leaves a partial vacuum. Its main function is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume. There are several types of vacuum pumps. Some of them are better suited for specific purposes than others. However, there are some disadvantages to using a vacuum pump.
Application of vacuum pump
Vacuum pumps are invaluable tools in many industrial and scientific processes. They are often used to move gas and other harmful substances and to clear clogged drains. They are also used to support mechanical equipment. For example, they can be mounted on the engine of a motor vehicle or the power hydraulic component of an aircraft. No matter how they are used, they should fit the application.
The principle of a vacuum pump is to draw gas from a sealed chamber to create a partial vacuum. Over the years, vacuum pump technology has evolved from its original beginnings to its current form. Today, there are many types of vacuum pumps, including rotary vane pumps, momentum transfer pumps, and regeneration pumps.
The semiconductor industry is a major user of vacuum pumps. Among other applications, these pumps are commonly used for mounting circuit boards, securing components, blowing and jetting, and pumping. The use of renewable resources has paved the way for widespread semiconductor production, where vacuum pumps are crucial. This manufacturing shift is expected to boost vacuum pump sales across Europe. 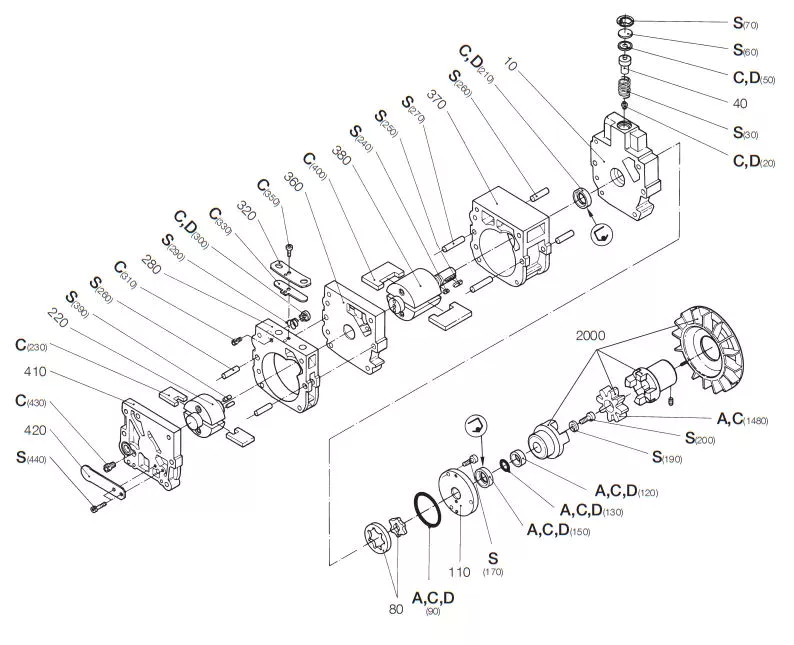
The most common types of vacuum pumps are positive displacement and rotary vane pumps. Positive displacement pumps are most effective for rough vacuum applications and are usually paired with momentum transfer pumps. These pumps are used in pharmaceutical, food and medical processes. They are also used in diesel engines, hydraulic brakes and sewage systems.
Positive displacement pumps are used to create low vacuum conditions and create a partial vacuum. These pumps create lower air pressure by enlarging the chamber and allowing gas to flow into the chamber. The air in the cavity is then vented to the atmosphere. Alternatively, momentum transfer pumps, also known as molecular pumps, use high-speed rotating blades to create dense fluids. 
Their drawbacks
Vacuum pumps are useful in industrial applications. However, they are not perfect and have some drawbacks. One of them is that their output is limited by the vacuum hose. Vacuum hoses are the bottleneck for vacuum pump performance and evacuation rates. The hose must be kept free of water and organic matter to ensure the highest possible vacuum.
Dry vacuum pumps do not have these problems. They may be more cost-effective but will increase maintenance costs. Water consumption is another disadvantage. When pond water is used, the pump puts additional pressure on the treatment facility. Additionally, contaminants from the gas can become trapped in the water, shortening the life of the pump.
Another disadvantage of vacuum pumps is their limited operating time at low vacuum. Therefore, they are only suitable for extremely high vacuum levels. Diaphragm pumps are another option for industrial applications. They have a sealed fluid chamber that allows a moderate vacuum. They also feature short strokes and a low compression ratio, making them quieter than their reciprocating counterparts.
Vacuum pumps are used in many industrial and scientific processes. They can be used to transport hazardous materials or clear clogged drains. They are also used in rear doors and dump tanks. Certain types of vacuum pumps can cause fluid blockages, which can be harmful. The vacuum pump should also be well suited to the fluid in it to avoid contamination.
Another disadvantage is the lack of proper vacuum system testing equipment. Mechanics often underestimate the importance of a properly functioning vacuum system. Most stores lack the equipment needed for proper troubleshooting. Typically, mechanics rely on the cockpit vacuum gauge to determine if the pump is working properly.
Some vacuum pumps are capable of providing constant vacuum. These pumps are also capable of eliminating odors and spills. However, these advantages are outweighed by some disadvantages of vacuum pumps.


editor by Dream 2024-05-15
China wholesaler 2be1406-1 Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump vacuum pump ac
Product Description
Product Description
2BE1 406-1 Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
2BE1 series liquid ring vacuum pumps and compressors are the products with high efficiency and economic power, which are manufactured by our company integrating with the advanced technology of the imported products from Germany.
These series products adopt CHINAMFG and single action structure and have many advantages, such as, compact structure, convenient maintenance, reliable running, high efficiency and economic power.
The main characteristics of 2BE1 series products:
All the bearings are the imported products with the brand name of CHINAMFG or NTN for ensuring the precise orientation and the high stability during the working of the pump.
The material of the impeller is QT400 nodular iron or stainless steel for ensuring the stability when the pump works under the rigorous condition and can extend the lifetime of the pump.
The casing is made of steel or stainless steel plates to extend the lifetime of the 2BE1 series pumps.
The shaft bushing is made of stainless steel to improve the lifetime of the pump 5 times than the normal material.
The V-belt pulley (when the pump is driven by the belt) is used the high precise pulley with taper bushing to keep the reliability of the pump and extend its life. And it is also easy to mantle and dismantle.
The coupling is used to drive the pump directly. The flexible part connecting the 2 half coupling is made of polyurethane that makes the pump more reliable.
The unique design to set the separator above the pump saves the space and decreases the noise efficiently.
All the parts are cast by the resin sands that make the pump surface very smooth. It is not necessary to cover the surface of the pumps with putty and gives out the heat efficiently.
The mechanical seals (optional) are used the imported products to avoid the leakage when the pump works for a long time.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| Type | Speed (Drive type) r/min |
Shaft power kW |
Motor power kW |
Motor type |
Limited vacuum mbar |
Suction capacity | Weight (Whole set) kg |
|
| m3/h | m3/min | |||||||
| 2BE1 151-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
10.8 7.2 9.2 13.2 14.8 |
15 11 11 15 18.5 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
405 300 360 445 470 |
6.8 5.0 6.0 7.4 7.8 |
469 428 444 469 503 |
| 2BE1 152-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
12.5 8.3 10.5 15.0 17.2 |
15 11 15 18.5 22 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
465 340 415 510 535 |
7.8 5.7 6.9 8.5 8.9 |
481 437 481 515 533 |
| 2BE1 153-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
16.3 10.6 13.6 19.6 22.3 |
18.5 15 18.5 22 30 |
Y180M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 Y200L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
600 445 540 660 700 |
10.0 7.4 9.0 11.0 11.7 |
533 480 533 551 601 |
| 2BE1 202-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(v) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
17 14 16 22 25 30 |
22 18.5 18.5 30 30 37 |
Y200L2-6 Y180M-4 Y180M-4 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
760 590 670 850 890 950 |
12.7 9.8 11.2 14.2 14.8 15.8 |
875 850 850 940 945 995 |
| 2BE1 203-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(V) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
27 20 23 33 37 45 |
37 30 30 45 45 55 |
Y250M-6 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225M-4 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1120 880 1000 1270 1320 1400 |
18.7 14.7 16.7 21.2 22.0 23.3 |
1065 995 995 1080 1085 1170 |
| 2BE1 252-0 | 740(D) 558(V) 660(V) 832(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
38 26 31.8 49 54 60 |
45 30 37 55 75 75 |
Y280M-8 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1700 1200 1500 1850 2000 2100 |
28.3 20.0 25.0 30.8 33.3 35.0 |
1693 1460 1515 1645 1805 1805 |
| 2BE1 253-0 | 740(D) 560(V) 660(V) 740(V) 792(V) 833(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
54 37 45 54 60 68 77 86 |
75 45 55 75 75 90 90 110 |
Y315M-8 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
2450 1750 2140 2450 2560 2700 2870 3571 |
40.8 29.2 35.7 40.8 42.7 45.0 47.8 50.3 |
2215 1695 1785 1945 1945 2055 2060 2295 |
| 2BE1 303-0 | 740(D) 590(D) 466(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
98 65 48 54 64 78 99 |
110 75 55 75 75 90 132 |
Y315L2-8 Y315L2-10 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
4000 3200 2500 2800 3100 3580 4000 |
66.7 53.3 41.7 46.7 51.7 59.7 66.7 |
3200 3200 2645 2805 2810 2925 3290 |
| 2BE1 305-1 2BE1 306-1 |
740(D) 590(D) 490(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
102 70 55 59 68 84 103 |
132 90 75 75 90 110 132 |
Y355M1-8 Y355M1-10 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
4650 3750 3150 3320 3700 4130 4650 |
77.5 62.5 52.5 55.3 61.2 68.8 77.5 |
3800 3800 2950 3000 3100 3300 3450 |
| 2BE1 353-0 | 590(D) 390(V) 415(V) 464(V) 520(V) 585(V) 620(V) 660(V) |
121 65 70 81 97 121 133 152 |
160 75 90 110 132 160 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5300 3580 3700 4100 4620 5200 5500 5850 |
88.3 59.7 61.7 68.3 77.0 86.7 91.7 97.5 |
4750 3560 3665 3905 4040 4100 4100 4240 |
| 2BE1 355-1 2BE1 356-1 |
590(D) 390(V) 435(V) 464(V) 520(V) 555(V) 585(V) 620(V) |
130 75 86 90 102 115 130 145 |
160 90 110 110 132 132 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6200 4180 4600 4850 5450 5800 6100 6350 |
103.3 69.7 76.7 80.8 90.8 98.3 101.7 105.8 |
5000 3920 4150 4160 4290 4300 4350 4450 |
| 2BE1 403-0 | 330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
97 110 131 160 203 234 |
132 132 160 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5160 5700 6470 7380 8100 8600 |
86.0 95.0 107.8 123.0 135.0 143.3 |
5860 5870 5950 6190 6630 6800 |
| 2BE1 405-1 2BE1 406-1 |
330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
100 118 140 170 206 235 |
132 160 185 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6000 6700 7500 8350 9450 15710 |
100.0 111.7 125.0 139.2 157.5 168.3 |
5980 6070 6200 6310 6750 6920 |
Company Profile
Greentech International (Xihu (West Lake) Dis.) Co.,Ltd is the professional supplier for CHINAMFG copy liquid ring vacuum pump and compressor. All our pumps are interchangeable with CHINAMFG both in dimension and performance. Most our client are using our pump to replace their existed CHINAMFG and CHINAMFG pump. Some clients are also buying our spare parts for original CHINAMFG pump repair.
As a CHINAMFG in vacuum pump field, the company has its own professional technical center, advanced equipment, foundry and machining workshop, assembling workshop and test center. Assure our products high quality, the company carry out 100% performance testing for all orders. Our strict quality control system and process guarantee that our products are produced according to the highest industrial standards, include casting material inspection, casting dimension inspection, welded part material inspection, dye penetrant inspection for welded parts, machining dimension inspection, balance testing for rotor, hydraulic pressure testing for casing and cover, dimension inspection for all finished parts before assembling.
Due to our high quality and competitive price, our pump are widely used for original CHINAMFG and CHINAMFG pump replacement in Mining industry, Electric power industry, petro chemical industry, pulp and paper industry, pharmaceutical industry, environment industry, food and beverage industry, Marine industry and other general industry process.
Our experienced and knowledgeable staff is dedicated to providing high quality products and after sales supports. Welcome clients to contact us and establish business relation ship.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Pre-Suction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Wet |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Semiconductor manufacturing involves the production of integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices used in various electronic applications. Vacuum pumps are used extensively throughout the semiconductor manufacturing process to create and maintain the required vacuum conditions for specific manufacturing steps.
Here are some key roles of vacuum pumps in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are used in deposition processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes involve depositing thin films of materials onto semiconductor wafers to create various layers and patterns. Vacuum pumps help create a low-pressure environment necessary for precise control of the deposition process, ensuring uniform and high-quality film formation.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps are utilized in etching and cleaning processes, which involve the removal of specific layers or contaminants from semiconductor wafers. Dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching, require a vacuum environment to facilitate the ionization and removal of material. Vacuum pumps aid in creating the necessary low-pressure conditions for efficient etching and cleaning processes.
3. Ion Implantation: Ion implantation is a process used to introduce impurities into specific regions of a semiconductor wafer to modify its electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the ion implantation chamber, creating the required vacuum environment for accurate and controlled ion beam acceleration and implantation.
4. Wafer Handling and Transfer: Vacuum pumps are employed in wafer handling and transfer systems. These systems utilize vacuum suction to securely hold and manipulate semiconductor wafers during various manufacturing steps, such as loading and unloading from process chambers, robotic transfer between tools, and wafer alignment.
5. Load Lock Systems: Load lock systems are used to transfer semiconductor wafers between atmospheric conditions and the vacuum environment of process chambers. Vacuum pumps are integral components of load lock systems, creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for wafer transfer while minimizing contamination risks.
6. Metrology and Inspection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in metrology and inspection tools used for characterizing semiconductor devices. These tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) and focused ion beam (FIB) systems, often operate in a vacuum environment to enable high-resolution imaging and accurate analysis of semiconductor structures and defects.
7. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are employed in leak detection systems to identify and locate leaks in vacuum chambers, process lines, and other components. These systems rely on vacuum pumps to evacuate the system and then monitor for any pressure rise, indicating the presence of leaks.
8. Cleanroom Environment Control: Semiconductor manufacturing facilities maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication process. Vacuum pumps are used in the design and operation of the cleanroom ventilation and filtration systems, helping to maintain the required air cleanliness levels by removing particulates and maintaining controlled air pressure differentials.
Vacuum pumps used in semiconductor manufacturing processes are often specialized to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. They need to provide high vacuum levels, precise control, low contamination levels, and reliability for continuous operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are indispensable in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the creation of the necessary vacuum conditions for various processes, ensuring the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.

Considerations for Selecting a Vacuum Pump for Cleanroom Applications
When it comes to selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, several considerations should be taken into account. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Cleanrooms are controlled environments used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and microelectronics. These environments require strict adherence to cleanliness and particle control standards to prevent contamination of sensitive processes or products. Selecting the right vacuum pump for cleanroom applications is crucial to maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the introduction of contaminants. Here are some key considerations:
1. Cleanliness: The cleanliness of the vacuum pump is of utmost importance in cleanroom applications. The pump should be designed and constructed to minimize the generation and release of particles, oil vapors, or other contaminants into the cleanroom environment. Oil-free or dry vacuum pumps are commonly preferred in cleanroom applications as they eliminate the risk of oil contamination. Additionally, pumps with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the potential for particle buildup.
2. Outgassing: Outgassing refers to the release of gases or vapors from the surfaces of materials, including the vacuum pump itself. In cleanroom applications, it is crucial to select a vacuum pump with low outgassing characteristics to prevent the introduction of contaminants into the environment. Vacuum pumps specifically designed for cleanroom use often undergo special treatments or use materials with low outgassing properties to minimize this effect.
3. Particle Generation: Vacuum pumps can generate particles due to the friction and wear of moving parts, such as rotors or vanes. These particles can become a source of contamination in cleanrooms. When selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, it is essential to consider the pump’s particle generation level and choose pumps that have been designed and tested to minimize particle emissions. Pumps with features like self-lubricating materials or advanced sealing mechanisms can help reduce particle generation.
4. Filtration and Exhaust Systems: The filtration and exhaust systems associated with the vacuum pump are critical for maintaining cleanroom standards. The vacuum pump should be equipped with efficient filters that can capture and remove any particles or contaminants generated during operation. High-quality filters, such as HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, can effectively trap even the smallest particles. The exhaust system should be properly designed to ensure that filtered air is released outside the cleanroom or passes through additional filtration before being reintroduced into the environment.
5. Noise and Vibrations: Noise and vibrations generated by vacuum pumps can have an impact on cleanroom operations. Excessive noise can affect the working environment and compromise communication, while vibrations can potentially disrupt sensitive processes or equipment. It is advisable to choose vacuum pumps specifically designed for quiet operation and that incorporate measures to minimize vibrations. Pumps with noise-dampening features and vibration isolation systems can help maintain a quiet and stable cleanroom environment.
6. Compliance with Standards: Cleanroom applications often have specific industry standards or regulations that must be followed. When selecting a vacuum pump, it is important to ensure that it complies with relevant cleanroom standards and requirements. Considerations may include ISO cleanliness standards, cleanroom classification levels, and industry-specific guidelines for particle count, outgassing levels, or allowable noise levels. Manufacturers that provide documentation and certifications related to cleanroom suitability can help demonstrate compliance.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their reliable and efficient operation. When choosing a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, consider factors such as ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and access to service and support from the manufacturer. Pumps with user-friendly maintenance features, clear service instructions, and a responsive customer support network can help minimize downtime and ensure continued cleanroom performance.
In summary, selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications requires careful consideration of factors such as cleanliness, outgassing characteristics, particle generation, filtration and exhaust systems, noise and vibrations, compliance with standards, and maintenance requirements. By choosing vacuum pumps designed specifically for cleanroom use and considering these key factors, cleanroom operators can maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the risk of contamination in their critical processes and products.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Laboratories?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are essential tools in laboratory settings as they enable scientists and researchers to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments. These controlled conditions are crucial for various scientific processes and experiments. Here are some key reasons why vacuum pumps are used in laboratories:
1. Evaporation and Distillation: Vacuum pumps are frequently used in laboratory evaporation and distillation processes. By creating a vacuum, they lower the boiling point of liquids, allowing for gentler and more controlled evaporation. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive substances or when precise control over the evaporation process is required.
2. Filtration: Vacuum filtration is a common technique in laboratories for separating solids from liquids or gases. Vacuum pumps create suction, which helps draw the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving the solid particles behind. This method is widely used in processes such as sample preparation, microbiology, and analytical chemistry.
3. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in freeze drying or lyophilization processes. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from a substance while it is in a frozen state, preserving its structure and properties. Vacuum pumps facilitate the sublimation of frozen water directly into vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture under low-pressure conditions.
4. Vacuum Ovens and Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in conjunction with vacuum ovens and chambers to create controlled low-pressure environments for various applications. Vacuum ovens are used for drying heat-sensitive materials, removing solvents, or conducting reactions under reduced pressure. Vacuum chambers are utilized for testing components under simulated space or high-altitude conditions, degassing materials, or studying vacuum-related phenomena.
5. Analytical Instruments: Many laboratory analytical instruments rely on vacuum pumps to function properly. For example, mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, surface analysis equipment, and other analytical instruments often require vacuum conditions to maintain sample integrity and achieve accurate results.
6. Chemistry and Material Science: Vacuum pumps are employed in numerous chemical and material science experiments. They are used for degassing samples, creating controlled atmospheres, conducting reactions under reduced pressure, or studying gas-phase reactions. Vacuum pumps are also used in thin film deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
7. Vacuum Systems for Experiments: In scientific research, vacuum systems are often designed and constructed for specific experiments or applications. These systems can include multiple vacuum pumps, valves, and chambers to create specialized vacuum environments tailored to the requirements of the experiment.
Overall, vacuum pumps are versatile tools that find extensive use in laboratories across various scientific disciplines. They enable researchers to control and manipulate vacuum or low-pressure conditions, facilitating a wide range of processes, experiments, and analyses. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-14
China Custom Industrial Vacuum Pump Air Oil Water Rotary Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pump with Great quality
Product Description
Industrial Vacuum Pump Air Oil Water Rotary Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pump
industrial vacuum pumps
Rotary vane: Rotary vane pumps are comprised of a series of vanes that are mounted to a rotor that turns inside a cavity. As the vanes rotate, centrifugal force extends them from their individual slots, forming compression cells that get larger to draw air in from the intake and smaller to push air out the exhaust.
Articulated piston: An articulated piston industrial vacuum pump operates in a manner similar to that of an automobile engine. As the piston moves downward inside the cylinder, air is drawn in through the intake valve. During the piston’s upward stroke, the air is permitted to escape via an exhaust valve. Two spring-backed piston rings are used to seal the piston to the cylinder.
Screw: Rotary screw pumnps include 2 parallel rotary screws in the pump housing. The screws are synchronized to turn in opposite directions, which causes the compression action to occur. The gas is compressed in the direction of the pump’s discharge port.
Liquid ring: Liquid ring pumps also operate via positive displacement. During operation, the pump’s impeller rotates inside the pump casing. A rotating liquid ring then seals the impeller and its blades. Liquid is sucked into the compression chamber to keep the ring stable. Conveyed gas is compressed during each impeller revolution.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What safety features are typically integrated into diaphragm vacuum pump systems?
Diaphragm vacuum pump systems typically incorporate various safety features to ensure safe operation and protect both the users and the equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Overpressure Protection: Diaphragm vacuum pump systems often include overpressure protection mechanisms to prevent excessive pressure buildup. These mechanisms can be in the form of pressure relief valves or pressure sensors that automatically shut off the pump or release excess pressure if it exceeds the predefined limits. Overpressure protection safeguards the system from potential damage and reduces the risk of accidents or equipment failure.
2. Thermal Protection: Thermal protection features are designed to prevent the pump from overheating. Diaphragm pumps can generate heat during operation, especially in continuous or intensive use. Thermal protection mechanisms, such as thermal switches or temperature sensors, monitor the pump’s temperature and automatically shut it down or activate cooling systems if the temperature exceeds safe limits. This helps prevent damage to the pump and reduces the risk of fire or other safety hazards.
3. Leak Detection: Diaphragm vacuum pump systems may incorporate leak detection mechanisms to alert users in case of any air or gas leakage. These mechanisms can include pressure sensors or flow sensors that monitor the system’s integrity. If a leak is detected, visual or audible alarms may be triggered, indicating the need for immediate attention and repair to maintain the system’s efficiency and prevent the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment.
4. Electrical Safety: Diaphragm pump systems have electrical safety features to protect against electrical hazards. This includes measures such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) or residual current devices (RCD) that detect and interrupt electrical faults, preventing electric shocks or short circuits. Proper grounding and insulation of electrical components are also important safety considerations in diaphragm pump systems.
5. Emergency Stop: Many diaphragm pump systems are equipped with an emergency stop button or switch that allows users to quickly shut down the pump in case of an emergency or hazardous situation. The emergency stop feature provides a convenient and immediate means to halt pump operation, ensuring the safety of the users and preventing further risks or damages.
6. System Monitoring and Alarms: Advanced diaphragm pump systems may incorporate monitoring features that continuously assess the system’s performance and provide real-time feedback. This can include monitoring parameters such as vacuum levels, temperature, pressure, or flow rates. Alarms or visual indicators are often integrated to alert users in case of deviations from normal operating conditions, enabling prompt corrective actions and preventing potential safety issues.
It’s important to note that the specific safety features integrated into diaphragm vacuum pump systems may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and intended application. Users should carefully review the product documentation and follow the manufacturer’s instructions regarding safety precautions, installation requirements, and maintenance procedures to ensure safe and proper use of the equipment.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pump systems typically incorporate safety features such as overpressure protection, thermal protection, leak detection, electrical safety measures, emergency stop functionalities, and system monitoring with alarms. These safety features aim to protect users, prevent equipment damage, and ensure the safe and reliable operation of the diaphragm pump system.

Are there variations in diaphragm vacuum pump designs, and how do they affect performance?
Yes, there are variations in diaphragm vacuum pump designs, and these variations can affect the performance of the pumps. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are available in different designs and configurations to meet specific application requirements. The design variations can impact several aspects of the pump’s performance, including:
– Pump Construction: Diaphragm vacuum pumps can have single or multiple diaphragms. Single diaphragm pumps typically offer a compact and lightweight design, making them suitable for portable applications. Multiple diaphragm pumps, on the other hand, provide higher flow rates and enhanced performance for applications that require greater pumping capacity.
– Materials of Construction: Diaphragm pumps can be constructed using various materials, including metals, plastics, and elastomers. The choice of materials affects the pump’s chemical compatibility, resistance to corrosion or abrasion, and overall durability. Selecting the appropriate materials is crucial to ensure reliable pump performance in specific operating conditions.
– Valve Design: The valves in diaphragm vacuum pumps play a critical role in controlling the direction of air flow and maintaining efficient pumping. Variations in valve design, such as the type of valves used (e.g., flapper valves, reed valves) and their configuration, can impact the pump’s suction capacity, vacuum level, and overall efficiency.
– Sealing Mechanisms: Diaphragm pumps employ various sealing mechanisms to ensure airtight operation and prevent air leakage. The sealing mechanisms can differ in terms of design, materials used, and effectiveness. Well-designed sealing mechanisms are necessary to maintain a consistent vacuum level and prevent loss of suction during operation.
– Control Features: Advanced diaphragm vacuum pumps may incorporate control features such as variable speed drives, pressure sensors, or automated systems for monitoring and adjusting pump performance. These control features can improve the pump’s efficiency, optimize energy consumption, and provide greater control over vacuum levels and flow rates.
The specific design variations in diaphragm vacuum pumps are often tailored to meet different application requirements, such as laboratory research, medical devices, or industrial processes. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the intended application and select a pump design that aligns with the desired performance parameters.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pumps come in various designs and configurations that can impact their performance. Factors such as pump construction, materials of construction, valve design, sealing mechanisms, and control features all contribute to the overall efficiency, reliability, and suitability of the pump for specific applications.

What are the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries?
Diaphragm vacuum pumps find widespread use in laboratories and various industries due to their versatile capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries:
In Laboratories:
– Laboratory Research and Analysis: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for various research and analytical applications. They provide vacuum conditions necessary for techniques such as filtration, degassing, rotary evaporation, centrifugation, and vacuum ovens. Diaphragm pumps are also used in analytical instruments like gas chromatographs, mass spectrometers, and vacuum-based sample preparation systems.
– Medical and Healthcare: Diaphragm pumps are employed in medical and healthcare settings for applications such as vacuum filtration in microbiology, vacuum aspiration in clinical laboratories, vacuum sealing of sterilized containers, and vacuum drying in medical device manufacturing. They are also used in dental clinics for suction and aspiration procedures.
– Environmental Monitoring and Analysis: Diaphragm vacuum pumps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring and analysis. They are used for air sampling, gas collection, and monitoring of pollutants in ambient air or emission sources. Diaphragm pumps are utilized in environmental testing laboratories for sample preparation and analysis, such as water and soil testing.
In Industries:
– Vacuum Filtration: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in industries for filtration processes. They create a vacuum to draw liquids through a filter medium, separating solids from the liquid. This technique is widely employed in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and chemical processing.
– Vacuum Drying and Degassing: Diaphragm pumps facilitate vacuum drying and degassing processes in industries. They help remove moisture or volatile substances from materials or products under vacuum conditions. This is crucial in industries like electronics manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and materials science.
– Automotive and Manufacturing Processes: Diaphragm vacuum pumps find applications in automotive and manufacturing processes. They are used for vacuum-assisted molding, vacuum lifting and handling of objects, vacuum packaging, and vacuum-based testing or leak detection in components and systems.
– Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing: Diaphragm pumps are extensively utilized in the semiconductor and electronics industry. They provide vacuum conditions for processes such as wafer handling, thin film deposition, etching, and packaging. Diaphragm pumps are preferred due to their oil-free operation, which prevents contamination of sensitive electronic components.
These are some of the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries. The versatility, oil-free operation, chemical resistance, and compact design of diaphragm pumps make them suitable for a wide range of applications, contributing to their popularity across various sectors.


editor by Dream 2024-05-13
China Professional Industrial Vacuum Pump High Pressure Air Blower Xgb Vortex Gas Air Pump CNC Machine Compressor Vacuum Pump for CNC Router Tableno Reviews Yet vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
Product Description
Customized support OEM
Place of Origin China
Power Source Electric
Structure Vacuum Pump
Warranty 1 year
Brand Name lq
Model Number customized
Horsepower /
Outlet Size /
Power /
motor /
Product name air pump
Voltage 380V
Warranty 1year
Material aluminium alloy
Type air
Keywords pump
MOQ 1set
frequency 50/60 Hz
phase 3 phase
Certification ce
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Product Name: | Air Pump |
|---|---|
| Voltage: | 380V |
| Warranty: | 1year |
| Material: | Aluminium Alloy |
| Type: | Air |
| Keywords: | Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
How to install a vacuum pump
A vacuum pump creates a relative vacuum within a sealed volume by drawing gas molecules from the sealed volume. Vacuum pumps can be used in a variety of industrial applications. They also offer various lubrication options. If you are considering purchasing, please understand its functions and features before purchasing.
How it works
The working principle of a vacuum pump is called gas transfer. The principle can be further divided into two basic categories: positive displacement and momentum transfer. At high pressure and moderate vacuum, gas molecules collide and move and create a viscous flow. At higher vacuum levels, gas molecules separate to create molecular or transitional flows.
Another principle of vacuum pumps is fluid-tightness. There are two main types of seals: rotary seals and screw seals. Rotary seals prevent liquid leakage, while screw seals only allow liquids to flow out at higher pressures. Some pumps may not use the third seal.
The flow rate of the vacuum pump determines the machine’s ability to pump a certain amount of material. A higher pumping speed will shorten the drain time. Therefore, the mass flow of the vacuum pump must be carefully considered. The speed and type of vacuum must also be considered.
The working principle of a vacuum pump is to push gas molecules from a high-pressure state to a low-pressure state. This creates a partial vacuum. There are many different types of vacuum pumps, each with different functions. Some are mechanical, some are chemical. In either case, their function is the same: to create a partial or complete vacuum. Vacuum pumps use a variety of technologies and are sized according to the application. Proper sizing is critical for optimum efficiency.
Gas transfer pumps use the same principles as vacuum pumps but use different technology. One of the earliest examples is the Archimedes spiral. Its structure consists of a single screw inside a hollow cylinder. More modern designs use double or triple screws. The rotation of the screw causes gas molecules to be trapped in the cavity between the screw and the housing. The fluid is then discharged at slightly above atmospheric pressure. This difference is called the compression ratio.
Another type of vacuum pump is a diffusion pump. Its main use is industrial vacuum processing. It is used in applications such as mass spectrometry, nanotechnology and analytical instrumentation. These pumps are generally inexpensive to purchase and operate.
Apply
Vacuum pumps are essential for many scientific and industrial processes. They are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, lamps and semiconductor processing. They can also be used to support mechanical equipment. For example, they can be mounted on the engine of a motor vehicle. Likewise, they can be used to power hydraulic components of aircraft. Among other uses, the vacuum pump helps calibrate the gyroscope.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry and are one of the largest users of this technology. They help deal with hazardous materials and eliminate waste quickly. They are also used in power jets, dump fuel tanks and rear doors, among others. However, they are sensitive to contamination and should only be used in environments where leaks can be prevented. Therefore, choosing the right fluid for the application is very important.
The most popular type of vacuum pump is the rotary vane pump. These pumps are known for their high pumping speed and low pressure. Their efficient pumping capacity allows them to reach pressures below 10-6 bar. Additionally, they are usually oil-sealed and have excellent vacuuming capabilities.
Vacuum pumps are often used to remove air from closed systems. They create a vacuum by reducing the density of the air in the compressed space. This is done by using the mechanical force energy generated by the rotating shaft. When the pump is under pressure, it converts this energy into pneumatic power. When the pressure is different, the energy produced depends on the volume of the gas and the pressure difference between the inner and outer atmospheres.
Vacuum pumps are also used in the manufacture of solar cells. They are used in the manufacture of solar cells, including ingot casting processes as well as cell and module processes. The design of the vacuum system plays an important role in reducing the cost of the process, thus making it profitable. Due to their low maintenance costs, they are an invaluable tool for making solar cells.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in many applications. In addition to industrial and research uses, they are also used in water remediation. 
Oil Lubrication Option
Vacuum pumps are available in a variety of oil lubrication options. Choosing the right lubricant can help protect your vacuum pump and maximize its performance. Different base oils may contain different additives, such as antioxidants, and some contain additional additives for specific purposes. You should choose an oil with the right concentration of these additives for optimal lubrication of your vacuum pump.
Vacuum pumps are usually lubricated with paraffinic mineral oil. However, this type of lubricant evaporates as the temperature increases. To minimize evaporative losses, choose a lubricant with low vapor pressure. Also, you should choose lubricants that are resistant to extreme temperatures. Extreme temperatures can put extra stress on the oil and can even significantly shorten the life of the oil.
In terms of viscosity, synthetic oils are the best choice for vacuum pumps. These types of oils are designed to resist gas dissolution and are more resistant to corrosion. Therefore, synthetic oils are ideal for handling aggressive substances. Whether or not your pump needs lubrication, choosing a quality product is important.
The vacuum pump oil should be changed periodically according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. If you use a filter, you should also change the oil as soon as the filter reaches the end of its life. Unplanned oil changes will eventually cause the vacuum pump to not reach its maximum vacuum capacity.
You can buy vacuum pump oil from vacuum pump manufacturers or other suppliers. These options are available in a variety of sizes, and labels can be customized. The oil should be designed for the pump. However, you should check the manufacturer’s recommendations to avoid buying the wrong type.
If you choose to use a synthetic oil, it is important to use a good quality oil. It helps the pump work more efficiently and prolong its life.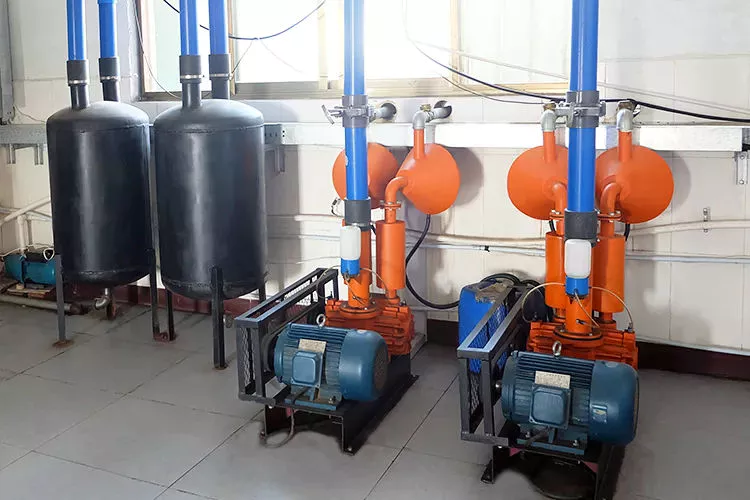 
Install
After choosing a suitable location, the next step is to install the pump. First, place the pump on a flat surface. Then, screw the pump onto the motor body above the check valve. Make sure the accessories are wrapped with sealing tape and secured with screws. The direction of gas inflow and outflow is indicated by arrows on the pump. The direction of rotation around the pump is also shown.
During commissioning, check the operation of each part of the pump. If the pump is equipped with a pipe connection, the pipe should be the same size and shape as the pump flange. Also, make sure that the piping does not cause any pressure drop. In addition, the first three weeks of operation require the installation of protective nets at the suction ports.
When selecting a pump, consider the back pressure of the system. Too much back pressure will affect the capacity of the vacuum pump. Also, check the temperature of the seal. If the temperature is too high, the seal may be damaged. It could also be due to a partially closed valve in the recirculation line or a clogged filter. Circulation pumps and heat exchangers should also be checked for fouling.
The vacuum pump is usually installed in the chassis area of the car. They can be mounted next to the engine or on a lower support frame. They are usually fastened to the bracket using suitable shock absorbers and isolating elements. However, before installing the vacuum pump, be sure to check the vacuum pump’s wiring harness before connecting it to the vehicle.
In many experimental setups, a vacuum pump is essential. However, improperly installed vacuum pumps can expose users to harmful vapors and chemicals. Appropriate plugs and belt guards should be installed to prevent any accidental chemical exposure. It is also important to install a fume hood for the pump.
In most cases, vacuum pumps come with installation manuals and instructions. Some manufacturers even offer start-up assistance if needed.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Best Sales C80-1.7 China Supply Cast Iron Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems at Power Plants. Alcohol Factory Multistage Air Blower vacuum pump ac
Product Description
CC80-1.7 China Supply Cast Iron Flue Gas Desulfurization Systems At Power Plants. Alcohol Factory Multistage Air Blower
Product Description
DECENT MACHINERY offers a full range of multistage centrifugal blowers with 20 models to choose from. We have the right blower for your application today and our Research and Development department is developing new models to meet your needs tomorrow.
Product performance ranges up to 98Kpa pressure or to -40Kpa vacuum and flows from 35 to 220 m³/min. Xihu (West Lake) Dis. manufactures blower and process control systems as well as provides complete blower packages with accessories to meet a wide variety of applications.
Series DM casting multistage centrifugal blower is a high efficient blower product which is developed by our company to introduce American technology and has advanced level in the world today.
This series of products adopts many proprietary or patented technologies, and the blower has much better performance than other competitors in lower noise level, lower vibration, and higher efficiency.
As a result for our constant concern to improve our performance and by investing a large part of our resources in research, Continental Industrie now presents a new high efficiency generation of between 1.000 to 65.000 m3/hr of a dry, clean, non pulsating air with pressures attaining 1,2 bar and vacuums up to 5500 mm H2O (WG).
| Mutistage Centrifugal Blower | Multi-Stage Centrifugal Fan | Multi-Stage Centrifugal Fan |
Application:
1. Water Treatment
2. Wastewater Treatment
3. Biogas Recovery
4. Vacuum Cleaning
5. Air Knife Dry
6. Floatation and Mineral Beneficiation
7. Galvanization Process and Electric Plating
8. Fluid and Piscina Oxygenation
9. Process Gas Conveying
10. Papermaking and Printing
11. Air Firing (Desulfurization, Carbon Black, Blast CZPT Process, and so on
Detailed Photos
The centrifugal blower housing consists of an inlet head with a special feature to direct air to the inlet of the first impeller and outlet head of special design to eliminate friction and multiple intermediate sections.
These parts are made in cast aluminum according to rigid Continental Industrie specifications, extreme care to be exercised in the assembly of interlocking cast aluminum intermediate sections and annular diffusers (baffles). The entire assembly is securely held together actually with multiple tension rods which bind the entire housing into a CZPT integral unit.
Product Parameters
Our Advantages
There are no parts in relative creep during operation. Since there is no friction and therefore no lubrication is necessary, the conveyed air is not polluted. Moreover, the main advantages of using Decent Machinery multistage centrifugal blowers are:
1.Easy Installation;
2.Low Noise Level;
3.No Vibration;
4.Pulsation Free Gas Flow;
5.No Gas Contamination;
6.Minimal Maintenance.
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Discharge Pressure Boost: | 9.8-117kpa |
|---|---|
| Relative Humidity: | 20-85% |
| Noise: | ≤84dB |
| Color: | Custom Made |
| Test: | Lab Testing |
| Transport Package: | Ply Woodcase |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Vacuum Packaging?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for vacuum packaging. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum packaging is a method used to remove air from a package or container, creating a vacuum environment. This process helps to extend the shelf life of perishable products, prevent spoilage, and maintain product freshness. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in achieving the desired vacuum level for effective packaging.
When it comes to vacuum packaging, there are primarily two types of vacuum pumps commonly used:
1. Single-Stage Vacuum Pumps: Single-stage vacuum pumps are commonly used for vacuum packaging applications. These pumps use a single rotating vane or piston to create a vacuum. They can achieve moderate vacuum levels suitable for most packaging requirements. Single-stage pumps are relatively simple in design, compact, and cost-effective.
2. Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are another popular choice for vacuum packaging. These pumps utilize multiple vanes mounted on a rotor to create a vacuum. They offer higher vacuum levels compared to single-stage pumps, making them suitable for applications that require deeper levels of vacuum. Rotary vane pumps are known for their reliability, consistent performance, and durability.
When using vacuum pumps for vacuum packaging, the following steps are typically involved:
1. Preparation: Ensure that the packaging material, such as vacuum bags or containers, is suitable for vacuum packaging and can withstand the vacuum pressure without leakage. Place the product to be packaged inside the appropriate packaging material.
2. Sealing: Properly seal the packaging material, either by heat sealing or using specialized vacuum sealing equipment. This ensures an airtight enclosure for the product.
3. Vacuum Pump Operation: Connect the vacuum pump to the packaging equipment or directly to the packaging material. Start the vacuum pump to initiate the vacuuming process. The pump will remove the air from the packaging, creating a vacuum environment.
4. Vacuum Level Control: Monitor the vacuum level during the packaging process using pressure gauges or vacuum sensors. Depending on the specific packaging requirements, adjust the vacuum level accordingly. The goal is to achieve the desired vacuum level suitable for the product being packaged.
5. Sealing and Closure: Once the desired vacuum level is reached, seal the packaging material completely to maintain the vacuum environment. This can be done by heat sealing the packaging material or using specialized sealing mechanisms designed for vacuum packaging.
6. Product Labeling and Storage: After sealing, label the packaged product as necessary and store it appropriately, considering factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure, to maximize product shelf life.
It’s important to note that the specific vacuum level required for vacuum packaging may vary depending on the product being packaged. Some products may require a partial vacuum, while others may require a more stringent vacuum level. The choice of vacuum pump and the control mechanisms employed will depend on the specific vacuum packaging requirements.
Vacuum pumps are widely used in various industries for vacuum packaging applications, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and more. They provide an efficient and reliable means of creating a vacuum environment, helping to preserve product quality and extend shelf life.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.

What Is the Purpose of a Vacuum Pump in an HVAC System?
In an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system, a vacuum pump serves a crucial purpose. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The purpose of a vacuum pump in an HVAC system is to remove air and moisture from the refrigerant lines and the system itself. HVAC systems, particularly those that rely on refrigeration, operate under specific pressure and temperature conditions to facilitate the transfer of heat. To ensure optimal performance and efficiency, it is essential to evacuate any non-condensable gases, air, and moisture from the system.
Here are the key reasons why a vacuum pump is used in an HVAC system:
1. Removing Moisture: Moisture can be present within an HVAC system due to various factors, such as system installation, leaks, or improper maintenance. When moisture combines with the refrigerant, it can cause issues like ice formation, reduced system efficiency, and potential damage to system components. A vacuum pump helps remove moisture by creating a low-pressure environment, which causes the moisture to boil and turn into vapor, effectively evacuating it from the system.
2. Eliminating Air and Non-Condensable Gases: Air and non-condensable gases, such as nitrogen or oxygen, can enter an HVAC system during installation, repair, or through leaks. These gases can hinder the refrigeration process, affect heat transfer, and decrease system performance. By using a vacuum pump, technicians can evacuate the air and non-condensable gases, ensuring that the system operates with the designed refrigerant and pressure levels.
3. Preparing for Refrigerant Charging: Prior to charging the HVAC system with refrigerant, it is crucial to create a vacuum to remove any contaminants and ensure the system is clean and ready for optimal refrigerant circulation. By evacuating the system with a vacuum pump, technicians ensure that the refrigerant enters a clean and controlled environment, reducing the risk of system malfunctions and improving overall efficiency.
4. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are also used in HVAC systems for leak detection purposes. After evacuating the system, technicians can monitor the pressure to check if it holds steady. A significant drop in pressure indicates the presence of leaks, enabling technicians to identify and repair them before charging the system with refrigerant.
In summary, a vacuum pump plays a vital role in an HVAC system by removing moisture, eliminating air and non-condensable gases, preparing the system for refrigerant charging, and aiding in leak detection. These functions help ensure optimal system performance, energy efficiency, and longevity, while also reducing the risk of system malfunctions and damage.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China Good quality Portable Water Pump for Home Irrigation and Outdoor Car Wash vacuum pump ac
Product Description
Small rechargeable pump, watering artifact, agricultural watering pump, irrigation watering vegetable, household garden watering machine
H03 lithium battery electric water pump
Power: 60W
Rated voltage: 12V
Charging voltage: 220V
Water output: 6-7L/min
Suction range: 2M
Water outlet distance: 55M
Battery specifications: 7.5AH, 10AH
Size: 315X200X255MM
weight: 3.5KG
Working time: 6AH 68minutes, 8AH 95minutes, 10AH 120minutes
Double motor double switch,Easy to replace the battery
| number | H03 |
| weight | 3.5KG |
| color | blue |
Portable water pump /Lithium battery water pump
It adopts dual-motor design and dual-switches. It can work with single motor or dual motor, with high efficiency and low energy consumption. The 7.5AH battery can work continuously for 60 minutes with the maximum water output. It is a good helper for vegetable gardens, gardens, grasslands, irrigation, and pesticide spraying. .
The product can choose 7.5AH or 10AH lithium battery, portable battery replacement, plug and play,with10m/20m/30m/40m/50m water outlet, it will stop when the gun is turned off, safe and reliable, net weight 3.5KGS, easy to carry.
Precautions
1: In order to ensure the use effect and joint tightness, please purchase Chaonongli original accessories!
2: Please place the product in a dry and ventilated place, do not put it in water or damp places or water, so as not to cause line oxidation and short circuit.
3: The machine is charged. The charging time limit for D1 is 5-6 hours, and the charging time limit for D2 and D3 is 6-8 hours. Please use the original Super Nongli charger, otherwise it is easy to cause abnormal power supply or short circuit of the machine.
4: Before charging the machine, make sure that the switch is off.
5: Before the product is used, the water inlet pipe and the water outlet joint must be inserted into the bottom of the machine plug, and all the threaded joints must be tightened, otherwise the joints are likely to leak water.
6: Before using the product, make sure that 1 end of the water inlet pipe has been plugged into the filter, otherwise it is easy to suck in foreign objects and cause abnormalities or damage to the machine.
7: If the product is used for pesticides, after use, the pesticides in the product need to be completely washed and drained out with clean water.
8: It is strictly forbidden to disassemble the product or battery without authorization.
9: It is strictly forbidden to change the parameters of the machine power supply system without permission;
Common problems and analysis solutions
1. The motor runs normally but does not absorb water:
a. The connection between the suction pipe and the water pump is not tight, or the water pipe is broken.
b. The small holes around the filter are blocked.
c. The internal parts of the water pump are worn out. It is recommended that the professional and technical personnel disassemble and replace the parts under the guidance of the professional and technical personnel, or foreign objects may affect the normal water absorption.
2. During use, the water output is sometimes large and sometimes small and makes abnormal noises:
a. If there is air in the water pump that has not been exhausted, the outlet pipe is not connected to the spray gun and the machine is turned on to exhaust the air.
b. The motors in the dual-core water pump are not synchronized. At this time, turn on a switch to observe whether the water is normal. If it is normal, first turn off and turn off I, then turn on switch II to observe whether the water is normal. Turn off switch II normally, and finally turn on both at the same time. A switch, whether the water outlet is normal.
3. The machine does not work and has no response:
a. The power supply has no electricity or poor contact.
b. The motor, switch and socket are damaged.
4. No water or low pressure from the nozzle:
a. There is a foreign body blockage inside the water pump or nozzle.
b. The battery voltage is insufficient.
5. Water leakage at the machine connection:
a. The connection is not tightened.
b. The sealing ring at the connection of the accessory is broken.
6. Reciprocating start when the machine is working (intelligent water pump):
a. There is a foreign body blockage inside the nozzle.
b. The water output of the sprinkler is too small, and it is close to the shut-off pressure set by the smart switch. It is recommended to use a water outlet with a larger aperture.
c. The pressure setting is too low.
Precautions for the use of the charger:
1 The charger must be kept away from rain and moisture. If water enters, it will be damaged
2 Do not use this charger to charge other batteries. If it does not match, it may cause a fire.
3 The charger should be kept clean, if dirt accumulates, it is easy to cause electric shock.
4 Before use, you must check the wires and plugs. If they are damaged, do not use them again. Do not disassemble without authorization. It can only be repaired by a professional engineer.
5 Do not place the charger on flammable products during charging, nor use it in a flammable environment. It will generate heat when charging, and it may cause a fire under the above conditions.
6 The voltage of the battery used must be consistent with the voltage indicated by the charger.
7 When repairing or cleaning, the plug must be unplugged
8 When the charger is not in use, please unplug it
9 Do not touch the non-insulated output connection part to prevent electric shock.
Portable water pump /Lithium battery water pump
It adopts dual-motor design and dual-switches. It can work with single motor or dual motor, with high efficiency and low energy consumption. The 7.5AH battery can work continuously for 60 minutes with the maximum water output. It is a good helper for vegetable gardens, gardens, grasslands, irrigation, and pesticide spraying. .
The product can choose 7.5AH or 10AH lithium battery, portable battery replacement, plug and play,with10m/20m/30m/40m/50m water outlet, it will stop when the gun is turned off, safe and reliable, net weight 3.5KGS, easy to carry.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 2 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Year |
| Max.Head: | 50-80m |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
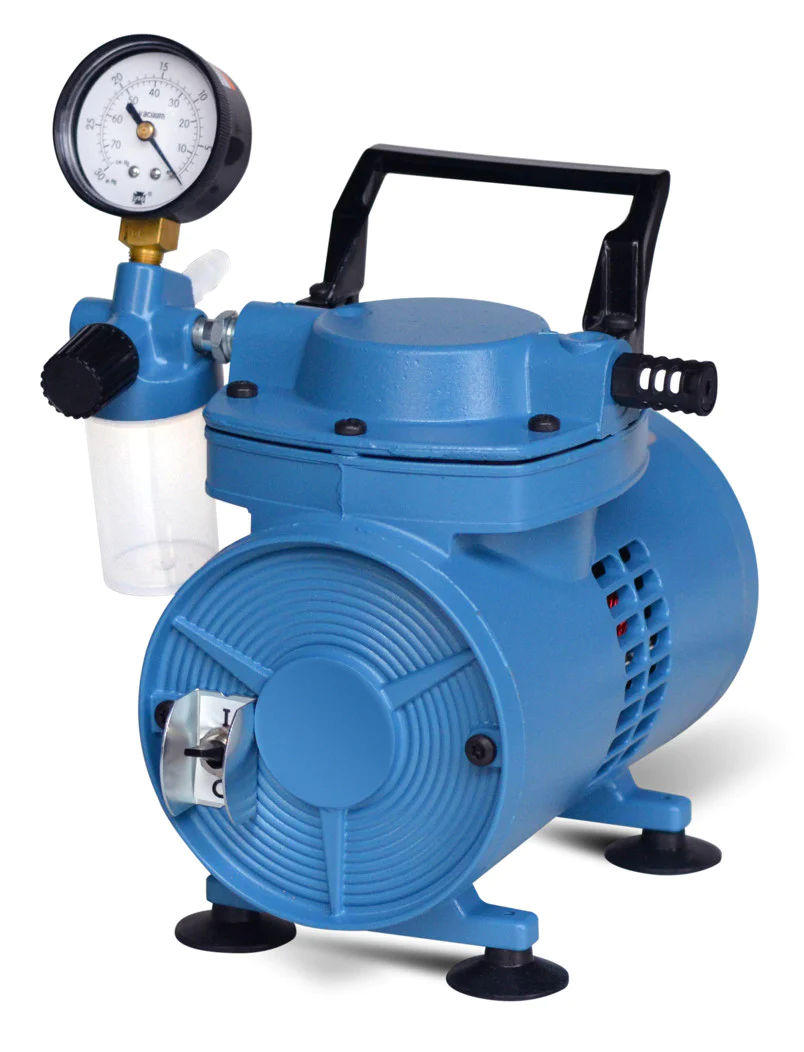

Can diaphragm vacuum pumps be integrated into existing laboratory setups and industrial processes?
Yes, diaphragm vacuum pumps can be integrated into existing laboratory setups and industrial processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Laboratory Setups: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratory environments for various applications, including filtration, aspiration, degassing, desiccation, and vacuum drying. They can be easily integrated into existing laboratory setups due to their compact size, versatility, and compatibility with a wide range of laboratory equipment.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps can connect to laboratory apparatus such as filtration systems, rotary evaporators, vacuum ovens, and vacuum desiccators. They often feature standard connections, such as hose barbs or quick-connect fittings, that allow for easy and secure attachment to different laboratory devices. In many cases, diaphragm vacuum pumps can directly replace other types of vacuum pumps without requiring significant modifications to the existing setup.
The ability to integrate diaphragm vacuum pumps into laboratory setups offers advantages such as:
– Oil-Free Operation: Diaphragm pumps do not require oil lubrication, eliminating the risk of oil contamination in the laboratory setup and reducing maintenance requirements.
– Quiet Operation: Diaphragm pumps are known for their relatively quiet operation, making them suitable for laboratory environments where noise reduction is desirable.
– Chemical Compatibility: Diaphragm pumps are available in models constructed with chemically resistant materials, allowing them to handle a wide range of solvents, gases, and vapors encountered in laboratory processes.
Industrial Processes: Diaphragm vacuum pumps can also be integrated into various industrial processes. They find applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, electronics, automotive, and materials processing.
In industrial settings, diaphragm vacuum pumps can be used for tasks such as vacuum packaging, degassing, solvent recovery, pneumatic conveying, and vacuum drying. They can be incorporated into existing process lines and equipment, providing the necessary vacuum levels and performance required for the specific application.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps offer advantages in industrial processes, including:
– Reliable Performance: Diaphragm pumps are known for their reliable operation, providing consistent vacuum levels and performance over time.
– Energy Efficiency: Diaphragm pumps can be designed to be energy-efficient, contributing to cost savings and sustainability in industrial operations.
– Low Maintenance: Diaphragm pumps generally have low maintenance requirements compared to other types of vacuum pumps, reducing downtime and operating costs.
When integrating diaphragm vacuum pumps into laboratory or industrial setups, it’s important to consider factors such as the required vacuum level, flow rate, compatibility with existing equipment, and any specific environmental or safety considerations. Additionally, consulting the manufacturer’s guidelines and seeking expert advice can ensure proper integration and optimal performance.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pumps can be easily integrated into existing laboratory setups and industrial processes. Their compact size, versatility, oil-free operation, chemical compatibility, and reliable performance make them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether in laboratory or industrial settings, diaphragm vacuum pumps offer advantages such as quiet operation, energy efficiency, and low maintenance requirements.

What is the noise level produced by diaphragm vacuum pumps during operation?
The noise level produced by diaphragm vacuum pumps during operation can vary depending on factors such as pump design, size, and operating conditions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally known for their relatively quiet operation compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The noise level produced by diaphragm pumps is typically lower than that of oil-sealed rotary vane pumps or piston pumps.
The noise level is influenced by various factors, including:
– Pump Design: The design of the diaphragm pump can affect the noise level. Some pumps are specifically engineered to minimize noise by incorporating features such as noise-reducing materials, vibration dampening mechanisms, or sound insulation.
– Pump Size and Power: Larger diaphragm pumps may generate more noise compared to smaller ones due to increased air displacement and higher power requirements. It’s important to consider the specific size and power rating of the pump when evaluating its noise level.
– Operating Conditions: The noise level can also be influenced by the operating conditions of the diaphragm pump. Factors such as speed, temperature, and the presence of vibrations or resonances in the system can impact the overall noise output.
While diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally considered to have low noise levels, it’s important to note that individual pump models may have different noise specifications. Manufacturers often provide noise level data in the pump’s technical documentation, which can help in selecting a pump that meets specific noise requirements.
Additionally, it’s worth considering noise reduction measures such as using vibration isolation pads, enclosing the pump in a soundproof housing, or employing remote mounting techniques to further minimize any noise generated by the pump.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pumps are known for their relatively quiet operation compared to other types of vacuum pumps. However, the actual noise level produced can vary depending on factors such as pump design, size, and operating conditions. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and implementing noise reduction measures can help ensure a suitable noise level for the intended application.

How do diaphragm vacuum pumps compare to other types of vacuum pumps in terms of performance?
When comparing diaphragm vacuum pumps to other types of vacuum pumps, several factors come into play that affect their performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how diaphragm vacuum pumps compare to other types in terms of performance:
1. Vacuum Level:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are capable of generating moderate vacuum levels, typically up to about 1 torr or 1 mbar. This makes them suitable for applications that require low to medium vacuum conditions. In comparison, other types of vacuum pumps such as rotary vane pumps or turbo molecular pumps can achieve much higher vacuum levels, extending into the ultra-high vacuum range.
2. Flow Rate:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps offer relatively lower flow rates compared to some other types of pumps. Their flow rates are typically in the range of a few liters per minute. This makes them well-suited for applications that require lower flow rates or when working with small sample sizes. However, if high flow rates are required, other types of pumps like rotary vane pumps or scroll pumps may be more suitable.
3. Contamination and Oil-Free Operation:
One significant advantage of diaphragm vacuum pumps is their oil-free operation. They do not require lubricating oil, which eliminates the risk of oil contamination in the pumped gas or vacuum environment. In comparison, oil-sealed pumps such as rotary vane pumps or oil diffusion pumps use oil as a lubricant and sealing medium, which can introduce oil vapor or particles into the vacuum system. This makes diaphragm pumps preferred in applications that require clean and uncontaminated vacuum conditions.
4. Chemical Resistance:
Diaphragm pumps are often designed with materials that offer excellent chemical resistance. This allows them to handle corrosive or reactive gases without degradation or contamination. In contrast, some other types of pumps may not be compatible with certain aggressive chemicals or may require additional protective measures. Diaphragm pumps are thus advantageous in applications that involve chemical processing or handling of corrosive gases.
5. Noise Level:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are known for their quiet operation compared to many other types of pumps. The reduced noise level contributes to a more comfortable working environment, making them suitable for applications where noise pollution needs to be minimized, such as laboratories or research facilities.
6. Maintenance and Lifespan:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps generally have relatively simple designs and require minimal maintenance. They do not have wearing parts like vanes or pistons that require regular replacement. This results in lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans compared to some other types of pumps. However, it’s important to note that the diaphragm itself may need periodic replacement due to wear and tear.
7. Cost:
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are typically more cost-effective compared to certain high-performance vacuum pumps such as turbo molecular pumps. They provide a good balance between performance and cost, making them suitable for a wide range of applications that do not require extreme vacuum levels or high flow rates.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing a vacuum pump. While diaphragm vacuum pumps may have some limitations in terms of vacuum level and flow rate compared to other types, their advantages in areas such as oil-free operation, chemical resistance, low noise, and cost-effectiveness make them a preferred choice in many applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China factory Vacuum Pump Air Fuel Injection Motor Aquarium Electric Syringe Hydraulic Electric Concrete Mixer and Mini Bicycle Irrigation Vacuum Pump vacuum pump ac
Product Description
Vacuum Pump Air Fuel Injection Motor Aquarium Electric Syringe Hydraulic Electric Concrete Mixer and Mini Bicycle Irrigation Vacuum Pump
Related products
Application of Vacuum Pump
Vacuum pumps find application in various industries and processes where the creation or maintenance of a vacuum is required. They remove gas or air from an enclosed space, creating a partial or complete vacuum. Here are some typical applications of vacuum pumps:
1. Industrial Processes: Vacuum pumps are utilized in various industrial processes, such as vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vacuum impregnation, and vacuum packaging. They help create a controlled environment with reduced pressure, allowing for removing moisture, contaminants, or unwanted gases from materials or products.
2. CZPT Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for refrigerant evacuation during installation, maintenance, or repair. They help remove air and moisture from the refrigeration system, ensuring optimal performance and preventing potential issues such as refrigerant contamination or system inefficiency.
3. Semiconductor Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in the semiconductor industry. They are used in thin film deposition, etching, and ion implantation, where a clean and controlled vacuum environment is essential for precise material deposition and device fabrication.
4. Laboratory Applications: Vacuum pumps are extensively utilized in laboratory settings for various applications. They are used in vacuum filtration, vacuum distillation, freeze-drying, degassing, and other processes that require the removal of gases or creating a controlled vacuum environment.
5. Medical and Healthcare: Vacuum pumps are applied in medical and healthcare facilities for various purposes. They are used in vacuum systems to suction fluids and gases during surgeries or medical procedures. Vacuum pumps are also employed in vacuum-assisted wound closure, where negative pressure promotes wound healing.
6. Food Processing and Packaging: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the food industry for vacuum packaging to extend the shelf life of perishable foods. They remove air from the packaging, reducing oxygen levels and inhibiting the growth of spoilage microorganisms. Vacuum pumps are also used in food processing applications such as freeze-drying, where moisture is removed from food products while maintaining quality.
7. Environmental Applications: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental monitoring and remediation processes. They are used in groundwater and soil remediation systems, where they help extract and remove contaminants. Vacuum pumps are also used in air sampling equipment to collect air samples in environmental monitoring studies.
8. Automotive Industry: Vacuum pumps find application in automotive systems, particularly in power brake systems. They create vacuum pressure to assist in brake actuation, ensuring efficient and responsive vehicle braking performance.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of vacuum pumps. The specific type and capacity of the vacuum pump may vary depending on the requirements of the particular process or industry. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, or scroll pumps, are chosen based on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, and compatibility with the process or application.
Company Profile
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Max.Head: | >150m |
| Max.Capacity: | >400 L/min |
| Driving Type: | Magnetic |
| Material: | Cast Iron |
| Samples: |
US$ 9999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Automotive Industry?
Yes, vacuum pumps are widely used in the automotive industry for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The automotive industry relies on vacuum pumps for several critical functions and systems within vehicles. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in enhancing performance, improving fuel efficiency, and enabling the operation of various automotive systems. Here are some key applications of vacuum pumps in the automotive industry:
1. Brake Systems: Vacuum pumps are commonly used in vacuum-assisted brake systems, also known as power brakes. These systems utilize vacuum pressure to amplify the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal, making braking more efficient and responsive. Vacuum pumps help generate the required vacuum for power brake assistance, ensuring reliable and consistent braking performance.
2. Emission Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are integral components of emission control systems in vehicles. They assist in operating components such as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve and the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for proper functioning of these systems, reducing harmful emissions and improving overall environmental performance.
3. HVAC Systems: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems in vehicles often utilize vacuum pumps for various functions. Vacuum pumps help control the vacuum-operated actuators that regulate the direction, temperature, and airflow of the HVAC system. They ensure efficient operation and precise control of the vehicle’s interior climate control system.
4. Turbocharger and Supercharger Systems: In performance-oriented vehicles, turbocharger and supercharger systems are used to increase engine power and efficiency. Vacuum pumps play a role in these systems by providing vacuum pressure for actuating wastegates, blow-off valves, and other control mechanisms. These components help regulate the boost pressure and ensure optimal performance of the forced induction system.
5. Fuel Delivery Systems: Vacuum pumps are employed in certain types of fuel delivery systems, such as mechanical fuel pumps. These pumps utilize vacuum pressure to draw fuel from the fuel tank and deliver it to the engine. While mechanical fuel pumps are less commonly used in modern vehicles, vacuum pumps are still found in some specialized applications.
6. Engine Management Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in engine management systems for various functions. They assist in operating components such as vacuum-operated actuators, vacuum reservoirs, and vacuum sensors. These components play a role in engine performance, emissions control, and overall system functionality.
7. Fluid Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in fluid control systems within vehicles, such as power steering systems. Vacuum-assisted power steering systems utilize vacuum pressure to assist the driver in steering, reducing the effort required. Vacuum pumps provide the necessary vacuum for power steering assistance, enhancing maneuverability and driver comfort.
8. Diagnostic and Testing Equipment: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in automotive diagnostic and testing equipment. These pumps create vacuum conditions necessary for testing and diagnosing various vehicle systems, such as intake manifold leaks, brake system integrity, and vacuum-operated components.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used depending on the specific automotive application. Common vacuum pump technologies in the automotive industry include diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and electric vacuum pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps have numerous applications in the automotive industry, ranging from brake systems and emission control to HVAC systems and engine management. They contribute to improved safety, fuel efficiency, environmental performance, and overall vehicle functionality.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.
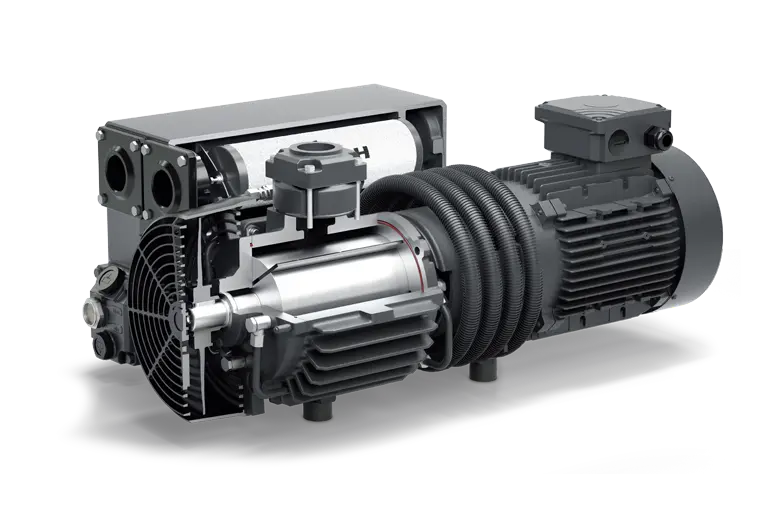
What Industries Commonly Rely on Vacuum Pump Technology?
Vacuum pump technology finds applications in various industries where creating and controlling vacuum or low-pressure environments is crucial. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Production: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in manufacturing and production processes across multiple industries. They are employed for tasks such as vacuum molding, vacuum packaging, vacuum degassing, vacuum drying, and vacuum distillation. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing rely on vacuum pump technology to achieve precise and controlled manufacturing conditions.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries heavily rely on vacuum pumps for numerous applications. These include solvent recovery, vacuum filtration, vacuum drying, distillation, crystallization, and evaporation. Vacuum pumps enable these industries to carry out critical processes under reduced pressure, ensuring efficient separation, purification, and synthesis of various chemical compounds and pharmaceutical products.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics: The semiconductor and electronics industries extensively use vacuum pumps for manufacturing microchips, electronic components, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps are crucial in processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etching, ion implantation, and sputtering. These processes require controlled vacuum conditions to ensure precise deposition, surface modification, and contamination-free manufacturing.
4. Research and Development: Vacuum pump technology is integral to research and development activities across scientific disciplines. It supports experiments and investigations in fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, biology, and environmental science. Vacuum pumps facilitate processes like freeze drying, vacuum distillation, vacuum evaporation, vacuum spectroscopy, and creating controlled atmospheric conditions for studying various phenomena.
5. Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry relies on vacuum pumps for packaging and preservation purposes. Vacuum sealing is used to extend the shelf life of food products by removing air and creating a vacuum-sealed environment that inhibits spoilage and maintains freshness. Vacuum pumps are also used in processes like freeze drying, vacuum concentration, and vacuum cooling.
6. Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, vacuum pumps play a role in various applications. They are used for crude oil vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vapor recovery, gas compression, and gas stripping processes. Vacuum pumps help maintain optimal conditions during oil refining, gas processing, and petrochemical manufacturing.
7. Environmental and Waste Management: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental and waste management applications. They are used for tasks such as soil vapor extraction, groundwater remediation, landfill gas recovery, and wastewater treatment. Vacuum pumps facilitate the removal and containment of gases, vapors, and pollutants, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable waste management.
8. Medical and Healthcare: The medical and healthcare sectors utilize vacuum pumps for various purposes. They are used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound therapy devices, vacuum-based laboratory analyzers, and vacuum suction systems in hospitals and clinics. Vacuum pumps are also used in medical research, pharmaceutical production, and medical device manufacturing.
9. Power Generation: Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation industries, including nuclear power plants and thermal power plants. They are used for steam condensation, turbine blade cooling, vacuum drying during transformer manufacturing, and vacuum systems for testing and maintenance of power plant equipment.
10. HVAC and Refrigeration: The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on vacuum pumps for system installation, maintenance, and repair. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from refrigerant lines and HVAC systems, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
These are just a few examples of industries that commonly rely on vacuum pump technology. The versatility and wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps make them indispensable tools across numerous sectors, enabling precise control over vacuum conditions, efficient manufacturing processes, and scientific investigations.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China best Oil-Lubricated Rotary Vane Blower Vacuum Pump for Medicine Technology vacuum pump ac
Product Description
DRV008D Double-stage,Oil-lubricated rotary vane vacuum pump,rotary piston pump,rotary vane blower
Pransch air rotary vane pumps have been the most popular pumps for generating low and medium vacuum for many years now. They are sturdy and have a long life, whether they are used as backing pumps to generate the backing pressure called for by turbopumps, or as a single standalone pump. Rotary vane pumps belong to the family of displacement pumps and convey a virtually steady low-pulsation suction volume flow, irrespective of the type of gas used. They work on the principle of an eccentrically supported rotor revolving in a housing, and have 2 or more movable vanes. Every CHINAMFG rotary vane vacuum pump is oil-lubricated. Special vacuum oils, also known as operating fluids, are responsible for insulating and lubricating components, resulting in very low final pressures. The oil lubrication also ensures an extremely long lifetime, even in continuous operation.
| Technical data | Frequency | DRV008D |
| Pumping Speed | 50Hz | 8m3/h |
| 60Hz | 9.6m3/h | |
| Ultimate Pressure w/o gas ballet | mbar | 4.0×10-4 |
| Ultimate total Pressure w/o gas ballet | mbar | 3.0×10-3 |
| Ultimate Pressure w/gas ballet | mbar | 6.0×10-3 |
| Water VaporΔP | mbar | 30 |
| Inlet/Outlet Flange | “ | KF25 |
| Voltage | 50Hz | 220/380v |
| 60Hz | 220/380v | |
| Nominal motor rating | Kw | 0.5 |
| Current | 50Hz | 9.57/5.40A |
| 60Hz | 11.5/6.48A | |
| Motor speed | 50Hz | 1440 |
| 60Hz | 1720 | |
| Noise | dB(A) | 54/56 |
| Oil (min/max) | L | 0.7/1.0 |
| Weight(w/o oil) | Kg | 27 |
Pransch Air two-stage rotary vane pumps, Their long life and pumping speed, irrespective of the gas used, are the outstanding properties of these pumps. Two-stage rotary vane pumps can be used in the pressure range between 100 hPa and a pressure roughly a decade above the final pressure. they are available in a standard version with a shaft seal for use in straightforward applications. also additionally available as an instrumentation version for more sophisticated applications, such as frequent cyclical pump-down processes (load locks). There are various corrosive versions available for pumping aggressive media.
Typical applications are found in widely ranging sectors:
- Analytics (mass spectrometry, electron microscopy)
- Coating technology (surface protection, decorative films, display units, monitor screens)
- Medicine/pharmaceutical technology (plasma sterilization, CHINAMFG drying)
- Vacuum metallurgy (vacuum soldering, vacuum sintering, vacuum alloys, CHINAMFG construction)
- Leak detection technology (vacuum systems, automotive tanks, airbag cartridges, packaging)
- Research institutes (elementary particle physics, CHINAMFG research, laser applications)
- Lighting industry (light bulb manufacture)
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Maintain the Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
How Do Vacuum Pumps Contribute to Energy Savings?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in energy savings in various industries and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through several mechanisms and efficiencies. Some of the key ways in which vacuum pumps help conserve energy are:
1. Improved Process Efficiency: Vacuum pumps are often used to remove gases and create low-pressure or vacuum conditions in industrial processes. By reducing the pressure, vacuum pumps enable the removal of unwanted gases or vapors, improving the efficiency of the process. For example, in distillation or evaporation processes, vacuum pumps help lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate or distill at lower temperatures. This results in energy savings as less heat is required to achieve the desired separation or concentration.
2. Reduced Energy Consumption: Vacuum pumps are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy compared to other types of equipment that perform similar functions. Modern vacuum pump designs incorporate advanced technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy-efficient motors, and optimized control systems. These features allow vacuum pumps to adjust their operation based on demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower process requirements. By consuming less energy, vacuum pumps contribute to overall energy savings in industrial operations.
3. Leak Detection and Reduction: Vacuum pumps are often used in leak detection processes to identify and locate leaks in systems or equipment. By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps can assess the integrity of a system and identify any sources of leakage. Detecting and repairing leaks promptly helps prevent energy wastage associated with the loss of pressurized fluids or gases. By addressing leaks, vacuum pumps assist in reducing energy losses and improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: In some applications, vacuum pumps can be integrated into energy recovery systems. For instance, in certain manufacturing processes, the exhaust gases from vacuum pumps may contain heat or have the potential for energy recovery. By utilizing heat exchangers or other heat recovery systems, the thermal energy from the exhaust gases can be captured and reused to preheat incoming fluids or provide heat to other parts of the process. This energy recovery approach further enhances the overall energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
5. System Optimization and Control: Vacuum pumps are often integrated into centralized vacuum systems that serve multiple processes or equipment. These systems allow for better control, monitoring, and optimization of the vacuum generation and distribution. By centralizing the vacuum production and employing intelligent control strategies, energy consumption can be optimized based on the specific process requirements. This ensures that vacuum pumps operate at the most efficient levels, resulting in energy savings.
6. Maintenance and Service: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their optimal performance and energy efficiency. Routine maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of pump components. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, prompt repair of any faulty parts or addressing performance issues helps maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevents energy waste.
In summary, vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, leak detection and reduction, integration with energy recovery systems, system optimization and control, as well as proper maintenance and service. By utilizing vacuum pumps efficiently and effectively, industries can minimize energy waste, optimize energy usage, and achieve significant energy savings in various applications and processes.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-08
China Custom Capacity 23100cbm/H Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
| Model |
Speed (r/min) |
Motor Power (KW) |
Limit Vacuum (hPa/mbar) |
Max. Capacity (m³/h) |
Weight (Kg) |
| 2BEC40 | 300 | 75 | 160 | 4256 | 3430 |
| 340 | 90 | 4920 | |||
| 390 | 110 | 5650 | |||
| 440 | 132 | 6300 | |||
| 490 | 132 | 6900 | |||
| 530 | 160 | 7500 | |||
| 570 | 185 | 8000 | |||
| 2BEC42 | 300 | 90 | 160 | 5740 |
3710 |
| 340 | 110 | 6375 | |||
| 390 | 132 | 7600 | |||
| 440 | 160 | 8550 | |||
| 490 | 185 | 9400 | |||
| 530 | 220 | 10130 | |||
| 2BEC50 | 260 | 160 | 160 | 8800 | 5400 |
| 300 | 185 | 10150 | |||
| 340 | 220 | 11400 | |||
| 380 | 250 | 12620 | |||
| 420 | 280 | 13880 | |||
| 2BEC52 | 230 | 160 | 160 | 9300 | 6000 |
| 260 | 185 | 10700 | |||
| 300 | 220 | 12400 | |||
| 340 | 250 | 14000 | |||
| 2BEC60 | 200 | 160 | 160 | 11000 | 8200 |
| 230 | 220 | 12780 | |||
| 260 | 280 | 14550 | |||
| 290 | 315 | 16050 | |||
| 2BEC67 | 180 | 220 | 160 | 15200 | 11390 |
| 210 | 250 | 18150 | |||
| 240 | 280 | 20650 | |||
| 270 | 355 | 23100 | |||
| 2BEC72 | 170 | 280 | 160 | 19000 | 14150 |
| 190 | 355 | 21600 | |||
| 210 | 400 | 23800 | |||
| 240 | 500 | 27000 |
2BE series liquid ring vacuum pump
2BE series liquid ring vacuum pump and compressor are designed according to international advanced technology and lots of practical experiences. It is a kind of highly effective and energy saving products.Usually it is uesed to pump some non-solid pellet,some gas which are not dissoluted in water,and has no corrosion so as to make vacuum and pressure in sealed containers. It is also used to pump some corrosion,flammable,explosive gas by some strcuture material changement and using expsion-proof electrical machinery. its strucure is simple and easy for mending,does be a kind of highly effective and energy saving products. It can be used widely ad papermaking ,chemical industry,petrification,light industry,medicines manufacture,food,metallurgy,building materials,coal washing,chemical fertilizer etc. some professions.Items:2BEA-103~2BEA-705 /2BEC-42~2BEC72,Motor power 11~630KW ,Capacity:290~27000M3/h Ultimate vacuum:-0.097~-0.084MPa.
Product’s Application
Product Display
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Warranty: | 12 Months |
|---|---|
| Oil or Not: | Water |
| Structure: | Singel Stage |
| Exhauster Method: | Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | Low Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Automotive Industry?
Yes, vacuum pumps are widely used in the automotive industry for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The automotive industry relies on vacuum pumps for several critical functions and systems within vehicles. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in enhancing performance, improving fuel efficiency, and enabling the operation of various automotive systems. Here are some key applications of vacuum pumps in the automotive industry:
1. Brake Systems: Vacuum pumps are commonly used in vacuum-assisted brake systems, also known as power brakes. These systems utilize vacuum pressure to amplify the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal, making braking more efficient and responsive. Vacuum pumps help generate the required vacuum for power brake assistance, ensuring reliable and consistent braking performance.
2. Emission Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are integral components of emission control systems in vehicles. They assist in operating components such as the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve and the Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) system. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for proper functioning of these systems, reducing harmful emissions and improving overall environmental performance.
3. HVAC Systems: Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems in vehicles often utilize vacuum pumps for various functions. Vacuum pumps help control the vacuum-operated actuators that regulate the direction, temperature, and airflow of the HVAC system. They ensure efficient operation and precise control of the vehicle’s interior climate control system.
4. Turbocharger and Supercharger Systems: In performance-oriented vehicles, turbocharger and supercharger systems are used to increase engine power and efficiency. Vacuum pumps play a role in these systems by providing vacuum pressure for actuating wastegates, blow-off valves, and other control mechanisms. These components help regulate the boost pressure and ensure optimal performance of the forced induction system.
5. Fuel Delivery Systems: Vacuum pumps are employed in certain types of fuel delivery systems, such as mechanical fuel pumps. These pumps utilize vacuum pressure to draw fuel from the fuel tank and deliver it to the engine. While mechanical fuel pumps are less commonly used in modern vehicles, vacuum pumps are still found in some specialized applications.
6. Engine Management Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in engine management systems for various functions. They assist in operating components such as vacuum-operated actuators, vacuum reservoirs, and vacuum sensors. These components play a role in engine performance, emissions control, and overall system functionality.
7. Fluid Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in fluid control systems within vehicles, such as power steering systems. Vacuum-assisted power steering systems utilize vacuum pressure to assist the driver in steering, reducing the effort required. Vacuum pumps provide the necessary vacuum for power steering assistance, enhancing maneuverability and driver comfort.
8. Diagnostic and Testing Equipment: Vacuum pumps are also utilized in automotive diagnostic and testing equipment. These pumps create vacuum conditions necessary for testing and diagnosing various vehicle systems, such as intake manifold leaks, brake system integrity, and vacuum-operated components.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may be used depending on the specific automotive application. Common vacuum pump technologies in the automotive industry include diaphragm pumps, rotary vane pumps, and electric vacuum pumps.
In summary, vacuum pumps have numerous applications in the automotive industry, ranging from brake systems and emission control to HVAC systems and engine management. They contribute to improved safety, fuel efficiency, environmental performance, and overall vehicle functionality.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Contribute to Energy Savings?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in energy savings in various industries and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through several mechanisms and efficiencies. Some of the key ways in which vacuum pumps help conserve energy are:
1. Improved Process Efficiency: Vacuum pumps are often used to remove gases and create low-pressure or vacuum conditions in industrial processes. By reducing the pressure, vacuum pumps enable the removal of unwanted gases or vapors, improving the efficiency of the process. For example, in distillation or evaporation processes, vacuum pumps help lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate or distill at lower temperatures. This results in energy savings as less heat is required to achieve the desired separation or concentration.
2. Reduced Energy Consumption: Vacuum pumps are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy compared to other types of equipment that perform similar functions. Modern vacuum pump designs incorporate advanced technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy-efficient motors, and optimized control systems. These features allow vacuum pumps to adjust their operation based on demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower process requirements. By consuming less energy, vacuum pumps contribute to overall energy savings in industrial operations.
3. Leak Detection and Reduction: Vacuum pumps are often used in leak detection processes to identify and locate leaks in systems or equipment. By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps can assess the integrity of a system and identify any sources of leakage. Detecting and repairing leaks promptly helps prevent energy wastage associated with the loss of pressurized fluids or gases. By addressing leaks, vacuum pumps assist in reducing energy losses and improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: In some applications, vacuum pumps can be integrated into energy recovery systems. For instance, in certain manufacturing processes, the exhaust gases from vacuum pumps may contain heat or have the potential for energy recovery. By utilizing heat exchangers or other heat recovery systems, the thermal energy from the exhaust gases can be captured and reused to preheat incoming fluids or provide heat to other parts of the process. This energy recovery approach further enhances the overall energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
5. System Optimization and Control: Vacuum pumps are often integrated into centralized vacuum systems that serve multiple processes or equipment. These systems allow for better control, monitoring, and optimization of the vacuum generation and distribution. By centralizing the vacuum production and employing intelligent control strategies, energy consumption can be optimized based on the specific process requirements. This ensures that vacuum pumps operate at the most efficient levels, resulting in energy savings.
6. Maintenance and Service: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their optimal performance and energy efficiency. Routine maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of pump components. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, prompt repair of any faulty parts or addressing performance issues helps maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevents energy waste.
In summary, vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, leak detection and reduction, integration with energy recovery systems, system optimization and control, as well as proper maintenance and service. By utilizing vacuum pumps efficiently and effectively, industries can minimize energy waste, optimize energy usage, and achieve significant energy savings in various applications and processes.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Food Processing?
Yes, vacuum pumps are widely used in food processing for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the food processing industry by enabling the creation and maintenance of vacuum or low-pressure environments. They offer several benefits in terms of food preservation, packaging, and processing. Here are some common applications of vacuum pumps in food processing:
1. Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in vacuum packaging processes. Vacuum packaging involves removing air from the packaging container to create a vacuum-sealed environment. This process helps extend the shelf life of food products by inhibiting the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms and reducing oxidation. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the air from the packaging, ensuring a tight seal and maintaining the quality and freshness of the food.
2. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps are essential in freeze drying or lyophilization processes used in food processing. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from food products while they are frozen, preserving their texture, flavor, and nutritional content. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment that allows frozen water to directly sublimate from solid to vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture from the food without causing damage or loss of quality.
3. Vacuum Cooling: Vacuum pumps are utilized in vacuum cooling processes for rapid and efficient cooling of food products. Vacuum cooling involves placing the food in a vacuum chamber and reducing the pressure. This lowers the boiling point of water, facilitating the rapid evaporation of moisture and heat from the food, thereby cooling it quickly. Vacuum cooling helps maintain the freshness, texture, and quality of delicate food items such as fruits, vegetables, and bakery products.
4. Vacuum Concentration: Vacuum pumps are employed in vacuum concentration processes in the food industry. Vacuum concentration involves removing excess moisture from liquid food products to increase their solids content. By creating a vacuum, the boiling point of the liquid is reduced, allowing for gentle evaporation of water while preserving the desired flavors, nutrients, and viscosity of the product. Vacuum concentration is commonly used in the production of juices, sauces, and concentrates.
5. Vacuum Mixing and Deaeration: Vacuum pumps are used in mixing and deaeration processes in food processing. In the production of certain food products such as chocolates, confectioneries, and sauces, vacuum mixing is employed to remove air bubbles, achieve homogeneity, and improve product texture. Vacuum pumps aid in the removal of entrapped air and gases, resulting in smooth and uniform food products.
6. Vacuum Filtration: Vacuum pumps are utilized in food processing for vacuum filtration applications. Vacuum filtration involves separating solids from liquids or gases using a filter medium. Vacuum pumps create suction that draws the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving behind the solid particles. Vacuum filtration is commonly used in processes such as clarifying liquids, removing impurities, and separating solids from liquids in the production of beverages, oils, and dairy products.
7. Marinating and Brining: Vacuum pumps are employed in marinating and brining processes in the food industry. By applying a vacuum to the marinating or brining container, the pressure is reduced, allowing the marinade or brine to penetrate the food more efficiently. Vacuum marinating and brining help enhance flavor absorption, reduce marinating time, and improve the overall taste and texture of the food.
8. Controlled Atmosphere Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in controlled atmosphere packaging (CAP) systems in the food industry. CAP involves modifying the gas composition within food packaging to extend the shelf life and maintain the quality of perishable products. Vacuum pumps aid in the removal of oxygen or other unwanted gases from the package, allowing the introduction of a desired gas mixture that preserves the food’s freshness and inhibits microbial growth.
These are just a few examples of how vacuum pumps are used in food processing. The ability to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments is a valuable asset in preserving food quality, enhancing shelf life, and facilitating various processing techniques in the food industry.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
China Standard Energy-Conserving Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps with Great quality
Product Description
Energy-Conserving Vacuum Pump Air Rotary Oil Water Piston Dry Portable Mini Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement DC AC Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps The installation of a Variable Speed Drive (VSD), sometimes called a variable frequency drive, usually saves between 50 and 65% in electricity costs with the same or better regulation of vacuum. The range of energy savings can be from 30 to 80 percent. They can be adapted to blower or in some cases rotary vane type vacuum pumps. They work by changing the speed of the vacuum pump based on the reading from a pressure sensor that is mounted on the vacuum line near the receiver jar. The VSD is basically a dedicated computer with many adjustments so it may be possible to improve vacuum regulation over the typical pneumatic vacuum regulator that only has a vacuum level adjustment. A VSD for a vacuum pump is usually economical for a dairy that milks a total of 8 hours or more per day. Typically a VSD will not be an economical option for small dairies due to less milking time and thus shorter vacuum pump run times but there are some other options to save energy costs.
company information
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
| Structure: | – |
| Exhauster Method: | – |
| Vacuum Degree: | – |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Are diaphragm vacuum pumps environmentally friendly and compliant with regulations?
Diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally considered to be environmentally friendly and compliant with regulations. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Environmental Friendliness: Diaphragm vacuum pumps offer several features that contribute to their environmental friendliness:
– No Oil Lubrication: Diaphragm pumps operate without the need for oil lubrication, which eliminates the risk of oil contamination in the vacuum system. This is particularly important in applications where oil vapor contamination could affect product quality or pose environmental hazards. The absence of oil lubrication also reduces the need for oil changes and disposal, resulting in lower environmental impact.
– Low Noise Emission: Diaphragm pumps are known for their relatively quiet operation compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The reduced noise emission makes them more environmentally friendly, particularly in settings where noise pollution needs to be minimized.
– Energy Efficiency: Diaphragm vacuum pumps can be designed to be energy-efficient, consuming less electrical power compared to other vacuum pump types. Reduced energy consumption not only contributes to cost savings but also helps reduce the overall environmental impact associated with energy usage.
– Chemical Compatibility: Diaphragm pumps are available in models constructed with chemically resistant materials. This allows them to handle corrosive gases or chemical vapors without degradation or release of harmful substances, further ensuring environmental compatibility.
Regulatory Compliance: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are designed and manufactured to meet regulatory standards and requirements. They are commonly used in various industries and applications where compliance with environmental and safety regulations is crucial. Some specific regulations that diaphragm vacuum pumps may comply with include:
– Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS): Diaphragm pumps are often manufactured to comply with RoHS directives, which restrict the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain flame retardants in electrical and electronic equipment.
– CE Marking: Diaphragm pumps intended for sale within the European Economic Area (EEA) are required to bear the CE marking, indicating compliance with relevant European Union (EU) directives related to health, safety, and environmental protection.
– International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards: Diaphragm vacuum pumps may adhere to specific IEC standards that ensure their safety, performance, and environmental compatibility.
It’s important to note that while diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally considered environmentally friendly and compliant with regulations, it’s essential to select pumps from reputable manufacturers and suppliers. This ensures that the pumps meet the necessary standards and certifications applicable to a specific industry or application.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pumps are environmentally friendly due to their oil-free operation, low noise emission, energy efficiency, and chemical compatibility. They are designed and manufactured to comply with regulatory standards and requirements, such as RoHS directives, CE marking, and IEC standards. When choosing diaphragm vacuum pumps, it’s advisable to verify that they come from reliable sources and meet the necessary certifications for your specific application to ensure environmental compatibility and regulatory compliance.

What are the maintenance requirements for diaphragm vacuum pumps, and are they user-friendly?
Diaphragm vacuum pumps have specific maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Maintenance requirements for diaphragm vacuum pumps typically include the following:
– Regular Inspection: Diaphragm pumps should be inspected regularly to check for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks. This includes inspecting the diaphragms, valves, seals, and other critical components for integrity and proper functioning. Regular inspections help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems.
– Cleaning: Keeping the pump clean is essential for efficient operation. It involves removing any accumulated dust, dirt, or debris from the pump’s exterior and ensuring that the air intake and exhaust ports are free from obstructions. Cleaning should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations using appropriate cleaning agents and techniques.
– Diaphragm Replacement: Over time, diaphragms in diaphragm vacuum pumps may wear out or become damaged. Regularly replacing worn or damaged diaphragms is crucial to maintain the pump’s performance. The frequency of diaphragm replacement depends on factors such as operating conditions, usage intensity, and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
– Lubrication: Some diaphragm pumps may require lubrication for certain components, such as bearings or moving parts. However, many diaphragm pumps are designed to operate without the need for lubrication, offering the advantage of reduced maintenance and eliminating the risk of oil contamination in sensitive applications.
– Seal Replacement: The seals used in diaphragm vacuum pumps may require periodic replacement to ensure airtight operation and prevent air leakage. The frequency of seal replacement depends on factors such as operating conditions and the manufacturer’s recommendations. It’s important to use high-quality replacement seals to maintain the pump’s performance and prevent any compromise in vacuum levels.
As for user-friendliness, diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally considered to be user-friendly due to the following reasons:
– Ease of Operation: Diaphragm pumps are designed for straightforward operation, typically involving simple on/off switches or control knobs. They often have intuitive interfaces that make them easy to use, even for individuals with limited technical expertise.
– Compact and Portable: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are often compact and lightweight, making them easy to handle and move around. Their small size and portable nature contribute to their user-friendliness, especially in applications where mobility is important.
– Minimal Maintenance: Compared to some other types of vacuum pumps, diaphragm pumps generally have lower maintenance requirements. They often do not require oil changes or complex maintenance procedures, reducing the time and effort needed for upkeep.
– Clear Documentation: Manufacturers provide user manuals and documentation that outline maintenance procedures, troubleshooting guides, and safety precautions. These resources help users understand the maintenance requirements and ensure that the pumps are operated and maintained correctly.
While diaphragm vacuum pumps are generally user-friendly, it’s important to note that proper training and adherence to safety guidelines are still necessary to ensure safe and effective operation. Following the manufacturer’s instructions and seeking professional assistance when needed are essential for maintaining the pump’s performance and extending its lifespan.
In summary, diaphragm vacuum pumps have specific maintenance requirements, including regular inspection, cleaning, diaphragm replacement, and seal replacement. They are generally considered user-friendly due to their ease of operation, compact design, minimal maintenance needs, and clear documentation provided by manufacturers.

What are the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries?
Diaphragm vacuum pumps find widespread use in laboratories and various industries due to their versatile capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries:
In Laboratories:
– Laboratory Research and Analysis: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for various research and analytical applications. They provide vacuum conditions necessary for techniques such as filtration, degassing, rotary evaporation, centrifugation, and vacuum ovens. Diaphragm pumps are also used in analytical instruments like gas chromatographs, mass spectrometers, and vacuum-based sample preparation systems.
– Medical and Healthcare: Diaphragm pumps are employed in medical and healthcare settings for applications such as vacuum filtration in microbiology, vacuum aspiration in clinical laboratories, vacuum sealing of sterilized containers, and vacuum drying in medical device manufacturing. They are also used in dental clinics for suction and aspiration procedures.
– Environmental Monitoring and Analysis: Diaphragm vacuum pumps play a crucial role in environmental monitoring and analysis. They are used for air sampling, gas collection, and monitoring of pollutants in ambient air or emission sources. Diaphragm pumps are utilized in environmental testing laboratories for sample preparation and analysis, such as water and soil testing.
In Industries:
– Vacuum Filtration: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in industries for filtration processes. They create a vacuum to draw liquids through a filter medium, separating solids from the liquid. This technique is widely employed in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and chemical processing.
– Vacuum Drying and Degassing: Diaphragm pumps facilitate vacuum drying and degassing processes in industries. They help remove moisture or volatile substances from materials or products under vacuum conditions. This is crucial in industries like electronics manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and materials science.
– Automotive and Manufacturing Processes: Diaphragm vacuum pumps find applications in automotive and manufacturing processes. They are used for vacuum-assisted molding, vacuum lifting and handling of objects, vacuum packaging, and vacuum-based testing or leak detection in components and systems.
– Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing: Diaphragm pumps are extensively utilized in the semiconductor and electronics industry. They provide vacuum conditions for processes such as wafer handling, thin film deposition, etching, and packaging. Diaphragm pumps are preferred due to their oil-free operation, which prevents contamination of sensitive electronic components.
These are some of the typical applications of diaphragm vacuum pumps in laboratories and industries. The versatility, oil-free operation, chemical resistance, and compact design of diaphragm pumps make them suitable for a wide range of applications, contributing to their popularity across various sectors.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07